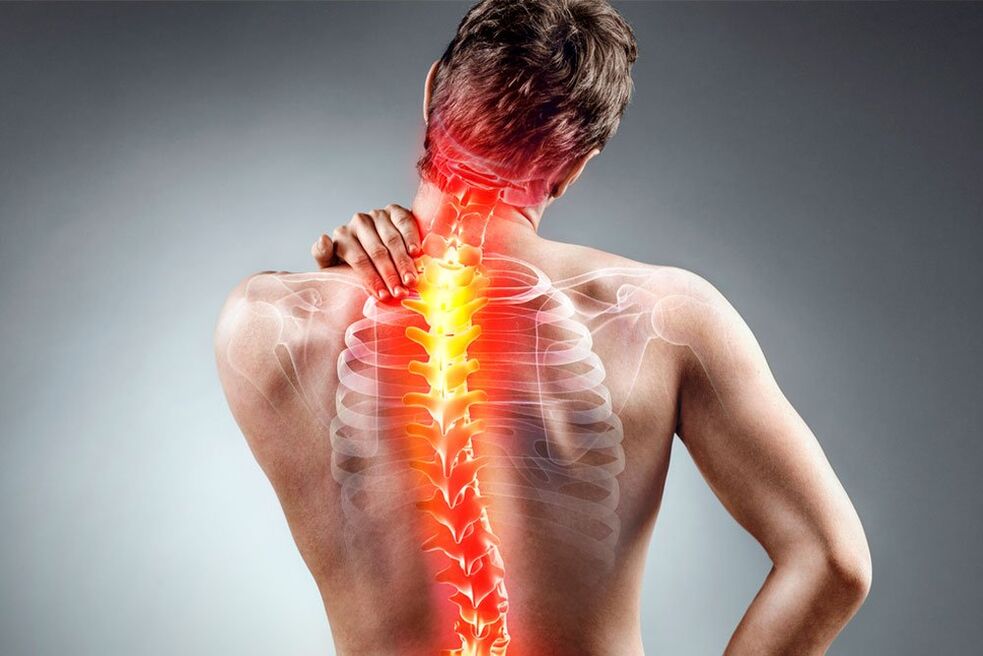
Osteochondrosis is a common disease of the musculoskeletal system. It manifests as slight discomfort and severe pain that limits a person's activity. In advanced cases, the pathology can lead to the need for surgery and even disability. Prevention and prevention of the disease reduces the risk of its occurrence or helps to achieve positive results of treatment.
Causes
Osteochondrosis is a pathology that occurs as a result of a combination of factors such as genetic predisposition, human lifestyle, environmental conditions.
The disease is characterized by damage to the articular cartilage, as well as the underlying bone tissue. Normally, it is the cartilage that provides the flexibility and mobility of the spine, but it can wear out, lose its properties, elasticity and deform under the pressure of other vertebrae.
The most common causes of the development of pathology are:
- hereditary predisposition.
- Muscle corset weakness.
- Postural disorders and scoliosis.
- Mechanical injury of the spine.
- Excessive physical activity.
- Neuroemotional stress.
- Passive lifestyle.
- Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract.
- Tight and uncomfortable shoes, high heels.
- General dehydration.
- Lack of important nutrients, beriberi.
Types of osteochondrosis
Cervical
This disease is included in the list of the most frequent complaints of patients of working age who spend up to 8-10 hours a day at the computer. Often patients do not attach importance to pain, which leads to the development of complications. If you do not want to experience constant pain in your neck, head and shoulders, it is important to prevent as soon as possible and, if necessary, consult a doctor as soon as possible.
thoracic
The disease can be asymptomatic. It is often accompanied by pain in the back, neck, and forearm. In the advanced stage, thoracic osteochondrosis is characterized by symptoms that are manifested by a painful condition of the arms and legs, tinnitus. Also, thoracic chondrosis may be accompanied by nausea, headache in the morning, pain and flickering in the eyes, sweating. For the treatment of the disease, taking medication and therapeutic exercises are sufficient measures.
Lumbar
The lumbar spine is very vulnerable. If you do not engage in strengthening your back muscles and do not monitor your posture, then there is a risk of developing unpleasant symptoms. Chondrosis is characterized by girdle pain in the lower back, pain in the hip region, and so-called back pain.
Take precautions. Keep your lower back warm, try not to make it too cold. Do not carry or lift objects weighing more than 10 kg. If you're lifting something heavy, don't jerk or jerk. Refuse any physical work in an inclined position. If you're going to mop the floor, use a mop or squat down.
Stages and symptoms of the development of osteochondrosis.
The disease goes through 4 stages, accompanied by various symptoms. In the initial stage, the pathology occurs in the region of the pulpal nucleus of the intervertebral disc. An excessive load causes a decrease in the height of the disc and the appearance of cracks in the annulus fibrosus. A person may feel a little discomfort when he is in a static position for a long time, or, on the contrary, when he moves too actively.
In the second stage, the distance between the vertebrae continues to decrease, the vertebral muscles and ligaments lose their tone and sag. This leads to increased mobility of the vertebrae with affected discs, the risk of displacement or subluxation. In the second stage, discomfort and pain appear, especially with certain types of loads or in certain positions.
With osteochondrosis of the third degree, prolapses and bulges of the intervertebral discs are formed, the development of arthrosis of the intervertebral joints is possible. A person experiences stiffness, becomes inactive. At this stage of the pathology, the pain is clearly felt depending on the location of the lesion.
In the fourth stage, the body tries to adapt to functional disorders of the spine. This can be expressed in bone neoplasms - osteophytes. They act as a fixator of vertebrae. But it can cause pinched nerves and other injuries.
Diagnostics
By examining a patient and taking a history, a specialist makes a primary diagnosis, suggesting the presence of a disease by a visually detectable curvature observed in the transverse or longitudinal plane of the spine. After the initial consultation, the surgeon or neurologist may prescribe additional tests. After determining the localization of the disease and its stages, you can begin treatment, the goal of which is to eliminate the causes of pain.
The most common diagnostic methods:
- bone scan;
- CONNECTICUT;
- magnetic resonance;
- doppler ultrasound.
Methods of treatment for osteochondrosis.
Treatment brings good results only when it is regular, consistent and systematic. The therapeutic strategy of the first stage is aimed at neutralizing pain, the second stage is to activate the blood supply and metabolic processes in the affected areas of the spine, and the third stage shows physiotherapy and manual procedures.
With osteochondrosis of any department in the acute stage, accompanied by severe pain, the doctor may prescribe a paravertebral blockade by administering novocaine, lidocaine and other drugs to relieve muscle tension in the moving segment of the spine, reduce swelling and tension muscular.
Combinations of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, antispasmodics, analgesics, and vitamin complexes (group D, nicotinic acid) are considered effective. As a local therapy, ointments are prescribed - chondroprotectors and agents with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory components.
It is important to remember that medications help to cope only with severe pain at the moment. Physiotherapy treatment helps to eliminate unpleasant manifestations of the disease in the long term.
The most commonly used therapies include:
- reflexology;
- acupuncture;
- electrophoresis;
- manual therapy;
- massage;
- physiotherapy.
What is the reason for the lack of treatment?
Osteochondrosis is best corrected at the initial stage of formation before the appearance of syndromes of vertebral pathologies, accompanied by chronic headaches and pain in the shoulder blades, heart and lower back. Over time, the disease leads to a change in the general structure of the spine due to active compensatory expansion of connective, fibrillar and bone tissues.
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the localization of the pathology, the degree of development of the process and the individual characteristics of the patients. Displacement of the intervertebral discs, protrusions and hernias have unpleasant consequences.
Frequent manifestations:
- violation of blood circulation in the tissues;
- pinched nerves;
- spinal canal dysfunction;
- edema and tissue fibrosis.
Therefore, the treatment of osteochondrosis should be started as soon as possible and carried out in a complex manner with an emphasis on neutralizing inflammation and eliminating pain. If the disease manifests itself for years, is at an advanced stage, and vertebral disc herniations are diagnosed, a surgical operation may be required.
Prevention
Prevention of osteochondrosis and its treatment are closely related to each other. Its goal is to improve the patient's quality of life. If you have a sedentary job, take regular breaks. Get up every hour and a half and do simple exercises that relieve tension in your neck and back muscles. Try to sit at the table correctly: your back is straight, your shoulders are relaxed. Choose such chairs, the back of which can provide maximum support for the spine: so that it does not overload.
To prevent the onset of the disease, it is good to periodically undergo a course of massage. Massage can improve blood circulation and lymph flow, improve metabolic processes in muscle tissues, and stop stagnant processes. As a result, there is an improvement in general well-being, increased vitality and some painful symptoms disappear.
Recommendations for the prevention and prevention of the development of osteochondrosis:
- Limit yourself when lifting weights. Admissible weight up to 10 kg.
- Carry weights evenly in both hands.
- Systematically perform simple exercises aimed at strengthening the spine, muscles, ligaments and joints.
- Go swimming if possible.
- Try not to sit for a long time in one position.
- Take dietary supplements that contain mucopolysaccharides, elements that build cartilage.
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the spine is a less difficult task than its subsequent treatment. Think about your health and start taking care of it before it reminds you of itself.